Symptoms and Food Precautions for Ulcerative Colitis
A 2019 study estimates that 700,000 people in the country have ulcerative colitis (UC), a disease where the intestine lining is inflamed and has ulcers. It is a type of inflammatory bowel disease, along with Crohn’s disease. Symptoms arise in flare-ups due to triggers like food and stress and recede in remission periods. Like any other illness, the prognosis is better when diagnosed earlier. This article details symptoms of ulcerative colitis and foods for it.
Warning Signs of Ulcerative Colitis
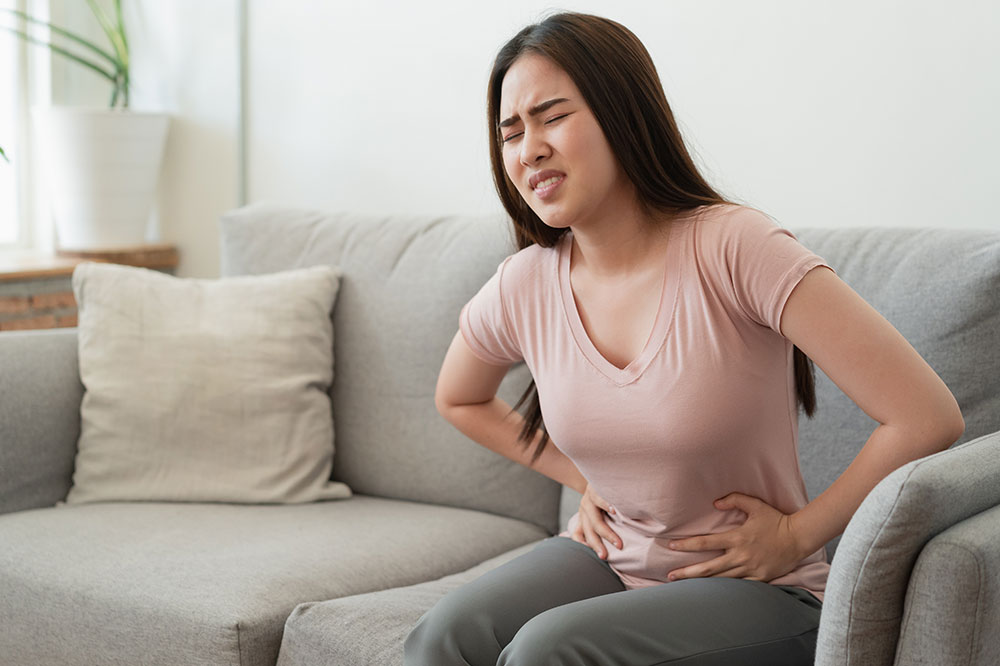
1. Stomach pain
While many people experience stomach pain, if you often feel it and cannot narrow it down to something you ate or attribute it to another illness, it could be ulcerative colitis.
2. Bloody stools
Since intestinal ulcers are at play, pus or blood in the stools is also a warning. The bowels may be loose, or you might have to use the restroom more than usual if you develop ulcerative colitis.
3. Weight loss
Long-term inflammation leads to weight loss. This can further be aggravated by abdominal pain and nausea that also reduces appetite. In children, lack of proper nourishment can lead to stunted growth.
4. Joint pain
Not all UC warning signs are gut-related. Some people may experience joint pain, skin sores, and anemia.
5. Fatigue
Fatigue and fever are not good signs and, if presenting in combination with any of the above, are indicators of ulcerative colitis.
Ulcerative Colitis and Food
UC symptoms can be brought on by stress, like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), but more often than not, flare-ups follow the consumption of certain foods. Doctors generally recommend an elimination diet. Over 73% of patients following this method achieve remission within 6-weeks. An elimination diet is a process where patients remove certain foods from their meals to see if the symptoms reduce, allowing them to identify individual triggers.
Food Precautions for Ulcerative Colitis
You can identify individual triggers only with an elimination diet or a food diary. Doctors, over the years, have identified specific common triggers that you can switch out or reduce in your regular meals.
1. Low-fiber diet
For most people, a low-fiber diet, consuming only 10-15 grams of fiber a day, seems to mitigate UC recurrence.
2. Alcohol
Alcohol and caffeinated and carbonated drinks are common triggers, as is dairy, especially in lactose-intolerant people.
3. Raw foods
Raw fruits and vegetables, dried fruits, and dried legumes also seem to be linked to UC flare-ups.
4. Sulfur and fiber
Foods rich in sulfur like eggs or those abundant in fiber, such as cabbage, are also common triggers of UC.
5. Seeds
It is best to avoid seeds, nuts, and nut butter and reduce meat and refined sugar intake.
6. Spicy food
Spicy food is another common UC trigger, as are sugar-free candies with sorbitol.
Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease
The warning signs for UC are very similar to those of Crohn’s disease. While UC affects only the large intestine, Crohn’s can happen anywhere in the GI tract. Hence UC symptoms and warning signs will be related to the bowels, and those of Crohn’s are more varied and can involve any part of the digestive tube from the mouth to the anus. Some warning signs of UC are as follows.